China's Foreign Trade to Achieve a Stable Growth with a Decreasing Rate
In the year of 2020,despite the impacts of COVID-19,China took the lead in recovering the economy,and as a result,imports and exports quickly stabilized,fully reflecting China’s strong capabilities in commodity supply. Amid the deep recession of the global economy,China became the primary driving force for global trade growth. Now with the recovery of the global economy and the continuous improvement of the domestic demand market,China’s foreign trade is expected to achieve steady growth in 2021,with a faster growth rate in the first half of the year and a slowdown in the second half. However,it is still exposed to a number of uncertainties,including repeated outbreaks of the pandemic,relocation of industrial chains,changes in the US policy towards China and the growingfluctuations of the renminbi exchange rate. In the short run,China should continue to implement foreign trade stabilization policies such as facilitating customs clearance and reducing corporate costs. In the long run,China should push the opening up to a higher level,like relaxing the restrictions for market access,promoting fair competition,improving the level of openness in systems for protection of intellectual property rights,bankruptcy and small and medium-sized enterprises,creating a market-oriented,law-based,internationalized business environment,and improving the economic and trade rules against the international ones,so as to lay a solid foundation for China’s foreign trade development.
Review of China’s Foreign Trade in 2020
In 2020,China’s foreign trade development mainly exhibited the following characteristics:
Firstly,China actively controlled the negative impacts of the pandemic,making its foreign trade quickly stabilized. According to the statistics released by the General Administration of Customs,in 2020,the total value of Chinese merchandise imports and exports amounted to 32.16 trillion yuan,a year-on-year increase of 1.9%. In particular,exports totaled 17.93 trillion yuan,a year-on-year increase of 4%; imports totaled 14.23 trillion yuan,a year-on-year decrease of 0.7%. The trade surplus expanded to 3.7 trillion yuan,an increase of 27.4% over the same period in 2019. Judging from the data of foreign trade in each month,China being the first in the world to resume production and work in March 2020 provided great support for the recovery of exports. In March,the decline in exports narrowed sharply from 15.8% in the previous two months to 3.5%. In April,exports began to see positive growth. So far,it has maintained positive growth for nine consecutive months. With the solid progress in domestic epidemic prevention and control and economic and social development,the effects of foreign trade stabilization policies started to show,and imports and exports gradually stabilized. In September,the cumulative growth rate of China’s imports and exports turned positive; and in November,the growth of exports in the US dollars reached 21.1%,the highest rate since February 2018 (see Figure 1).
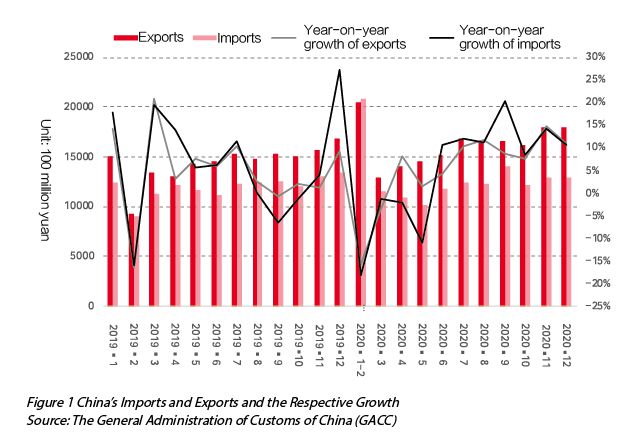
Secondly,China turned the crisis into opportunities - the export of epidemic prevention supplies and “stay at home” commodities increased substantially,showing China’s strength in commodity supply. In terms of export commodities,in 2020,the exports of textile products including masks exceeded 1 trillion yuan,a year-on-year increase of 30.4%,which was the biggest highlight of export growth in 2020. In addition to this,the exports of plastic products including gloves and protective clothing amounted to 590.2 billion yuan in 2020,a year-on-year increase of 20.0%. The exports of medical instruments and appliances also increased by up to 41.5%. At the same time,the pandemic brought changes in people’s lifestyles,leading to rapid growth in the exports of communication devices and other “stay at home” commodities exports. In 2020,China’s exports of automatic data processing equipment and their parts and components,including tablets and laptops,totaled 1.46 trillion yuan,a year-on-year increase of 12.0%; exports of toys were 231.7 billion yuan,a year-on-year increase of 7.7%; for household appliances,3.39 billion pieces were exported,amounting to 458.2 billion yuan,constituting an increase of 14.2% and 24.2%,respectively. In particular,the exports of refrigerators,electric fans,and vacuum cleaners all increased by more than 20% (see Figure 2).
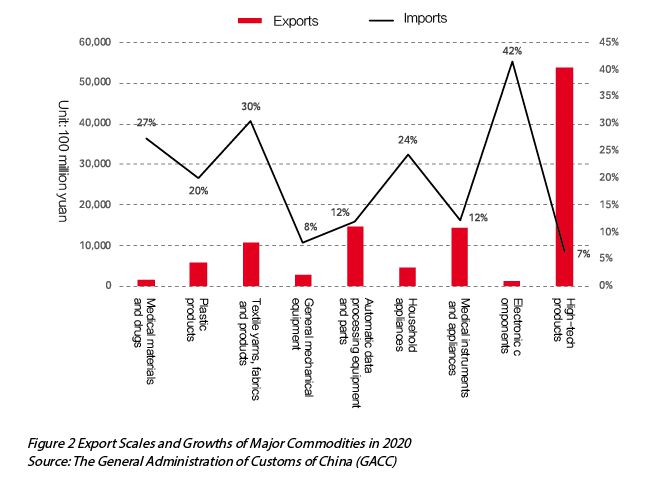
Thirdly,China carried out closer economic and trade exchanges with ASEAN,and its imports and exports maintained steady growth with major trading partners such as Europe and the United States. In terms of economic and trade exchanges with ASEAN,China’s imports and exports to ASEAN totaled 4.74 trillion yuan in 2020,an increase of 7% over the same period in 2019. This accounted for 14.7% of China’s total experts and imports,making ASEAN take the place of the EU as the largest trading partner of China. Specifically speaking,China’s exports to ASEAN were 2.66 trillion yuan,an increase of 7%; imports from ASEAN were 2.08 trillion yuan,an increase of 6.9% on a year-on-year basis. In recent years,driven by the low labor and land costs in ASEAN,some labor-intensive industries such as textile and garment,mechanical and electrical product processing and assembly in China have gradually relocated their facilities to ASEAN countries such as Vietnam. The trade exchanges of related intermediate products have driven the rapid growth of bilateral trade between China and ASEAN. With the conclusion of China-ASEAN Free Trade Area Upgrading Protocol in 2019,economic and trade exchanges between China and ASEAN countries have become more frequent,and the industrial chains have been further integrated. In the future,spurred on by the “Belt and Road” initiative and the multilateral framework of Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP),ASEAN will play an even more important role in China’s foreign trade. In addition to this,China’s imports and exports with major trading partners such as EU,the United States,Japan and South Korea also achieved positive growth. In 2020,China’s total imports and exports to the EU,the second largest trading partner,reached 4.5 trillion yuan,a year-on-year increase of 5.3%,accounting for 14.0% of China’s total imports and exports. China’s trade surplus with the EU narrowed to 921 billion yuan,a year-on-year decrease of 12.3% over 2019. The imports and exports to the United States totaled 4.06 trillion yuan,an increase of 8.8%. While the United States was still imposing high tariffs on nearly half of its imports from China,the exports to the United States from China achieved a rapid growth of 8.4% to 3.13 trillion yuan. Japan and South Korea are China’s fourth and fifth largest trading partners. In 2020,the bilateral trade between China and Japan and between China and South Korea also steadily increased by 1.2% and 0.7%,respectively.
Administration of Customs of China (GACC)
Fourthly,while the global economy was in deep recession,China became the primary driving force for the development of global trade. According to the latest data released by the World Trade Organization in last December,the world merchandise trade volume in the first three quarters fell by 8.2% compared with that in the same period of 2019. In the third quarter,the trade volume rebounded by 11.6% quarter-on-quarter,but it was still a decrease of 5.6% over the sam

