The Digitalization of Chinese SMEs and Its Economic Effects
Author:ZHENG Haitao, GAO Wei and REN Ruoen
The term “digital economy” refers to a series of economic activities that treat digital knowledge and information as key factors of production,make modern information networks as crucial carriers of productivity,and use information and communication technologies to increase efficiency and to optimize the economic structure. Currently,given the technological revolution,the adjustment of the economic structure and the outbreak of COVID-19 pandemic,the digital economy has become a new form of the economy,following the agricultural economy and the industrial economy.
According to China’s Digital Economy Development Report (2022),which was released by the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT),the total size of the Chinese digital economy reached 45.5 trillion yuan,accounting for 39.8% of GDP in 2021. In other words,the digital economy has played a crucial role in the development of the national economy.
In the context of the development of the digital economy,an increasing number of enterprises have gradually carried out a digital transformation. By using artificial intelligence,big data,cloud computing and other digital technologies,enterprises can transform and upgrade their organizational management,business circulation and other activities,as well as develop new competitive advantages. The current studies have shown that the application of digital technology can improve firm performance,accelerate the specialization of work and increase the achievements and efficiency. In addition,the application of digital technology not only promotes the development of enterprises but also has a significant effect on the macroeconomy.
The APEC SME Information Promotion Center,Beihang University and other units jointly released the 2021 Digital Index Report on Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises. The index measures the digitalization level of SMEs by measuring the breadth and depth of their application of digital and information technologies in their organization,business and industrial interactions. Drawing on this report,this article analyzes the characteristics of Chinese SMEs’ digital development and the impact of that digitalization on the macroeconomy.
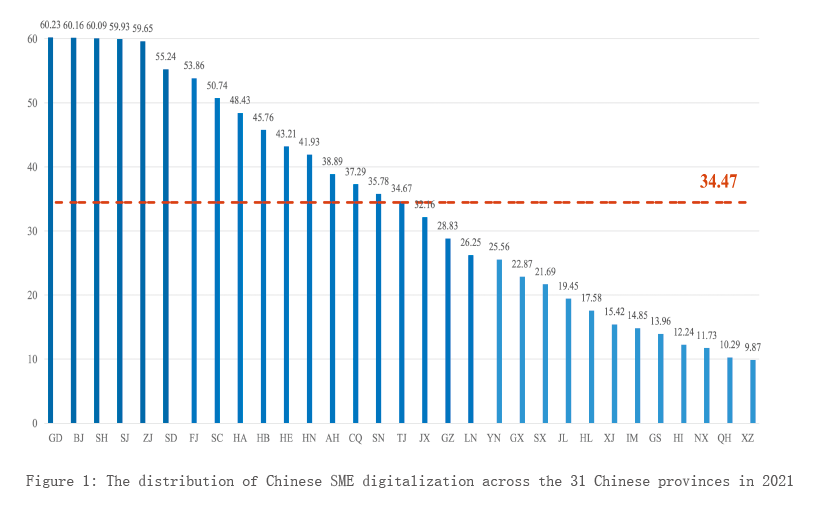
The digitalization of SMEs in China is unbalanced,with that in Jiangsu,Zhejiang,Shanghai and Beijing near the top
The distribution of Chinese SME digitalization as of 2021 across the 31 Chinese provinces is shown in Figure 1. In 2021,the average digitalization score for SMEs was 34.5 points,with 16 provinces having scores higher than this average score. Guangdong ranked first with 60.23 points,followed by Beijing,Shanghai,Jiangsu,Zhejiang and Shandong. Most of the higher scores provinces are located in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei,Yangtze River Delta and Pearl River Delta regions. The above regions account for approximately 42% of the China’s total GDP,and their excellent market and trade environments,rich talent pool,and technical support provide a strong environment for the digitalization of SMEs.
At the city level,the eight leading cities in China include Shenzhen,Guangzhou,Hangzhou,Suzhou,Chengdu,Nanjing,Wuhan and Ningbo. By analyzing the distribution of the top 100 cities in terms of SME digitalization,we can see that the digitalization of SMEs in China is imbalanced. First,the number of cities from different regions in the higher scores 100 cities varies greatly. Second,the development of SME digitalization is also imbalanced within a given region. In southeast China,Guangdong ranks at the top in terms of SME digitalization. However,the scores for nearby provinces,such as Guangxi and Hainan,do not even reach the average level. Overall,the development of SMEs digitalization in China is strong in the eastern and southern regions but weak in the western and northern regions. Moreover,the power of top-ranked cities in terms of SME digitalization to exert an impact on their neighboring cities is weak,which leads to extensive room for improvement in digitalization within a given region.
The digitalization of SMEs promotes urban economic development by enhancing innovation capacity
China’s 31 provinces can be divided into four digital economy categories according to the average digitalization score and to GDP (see Figure 2). Provinces in the top right (green) region are leading provinces,as both their digitalization level and their economy are better than the national average. The bottom-right (blue) region includes digital drivers. These areas have a high degree of digitalization,but their economies are underdeveloped. Provinces in the top-left (yellow) region are economic drivers,as their economies are better than average,but they need to exert more effort regarding digitalizatio

