The US Inflation May Remain Elevated for a Longer Period
The latest data shows that the US CPI increased by 8.5% year-to-year in July,and the month-on-month growth was flat. The CPI slowed down for the first time in two years,but remained high in the short term. From the perspective of the four major driving forces of the US inflation,the slowdown in global economic growth has quelled high oil prices,and the repair of supply chains has pushed down the prices of manufactured goods and food. However,the rising shelter cost has supported the strong demand for rents,and the hot job market has been bringing higher income and more demand. Looking ahead,a number of factors affecting the trend of inflation,including the impact of geopolitical conflicts on commodity prices,the reallocation of global industrial and supply chains,and the impact of economic recession on new employment and rental demand. Given that inflation is one of the core concerns of the Federal Reserve,it is important to further understand how it moves.
The US inflation is rising at an unprecedented pace
Since the first quarter of 2021,the CPI in the US has risen rapidly from less than 2% to 8.5% in July this year,among the strongest increase in more than 40 years. As a result,the Federal Reserve was forced to admit that monetary policy measures has lagged behind the market,and initiated the fastest rate hike since the tech bubble in 2001. From January to July this year,the Fed has raised interest rates by 225 basis points.
In regards to specific indicators,the widely used are PCE index and CPI. The weights that make up the sub-items of PCE index change quarter by quarter,and this makes PCE index the main policy reference for the Fed. In 2012,the Fed set a long-term inflation target of a 2% increase in core PCE. Although the inflation rate calculated by CPI is often higher and more volatile than PCE,considering that the Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers (CPI-U) is still widely used in financial market and cost adjustment and measures changes in US consumer prices based on a representative basket of goods and services. In this paper,CPI-U (hereinafter referred to as CPI) is taken as an example for analysis. Based on representative groups,CPI can be referred to CPI-W (covering the wage earners) and CPI-U (covering all workers). The latter covers a wider group and is the main concern of the market. Table below describes the comparison of sub-items between CPI and PCE index.
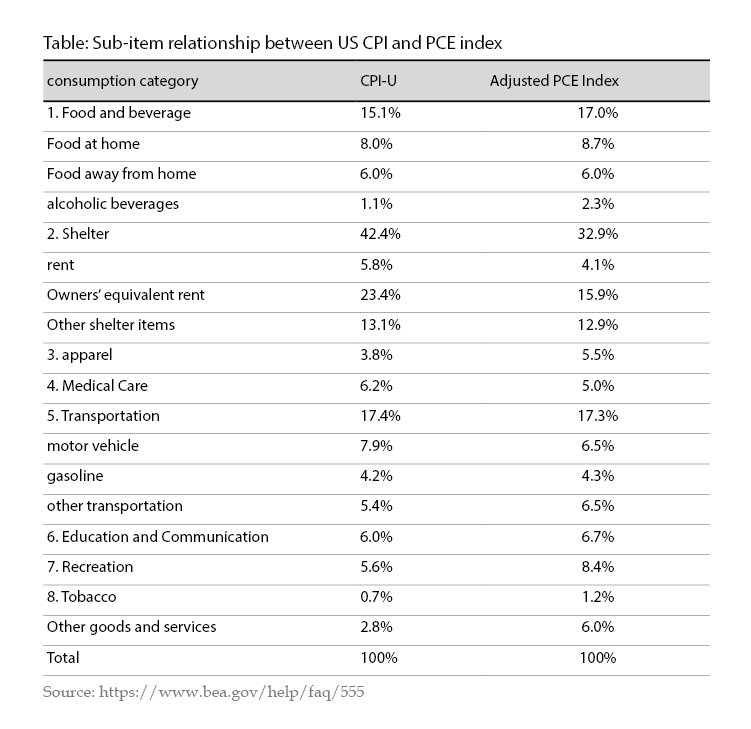
Dismantling the micro-factors of the inflation this year
The composition of the CPI has changes from commodity-based to service-based in the US. Since the energy and food prices are affected by the world market characterized as “white noise”,Bureau of Labor Statistics further introduces the concept of core and headline CPI. The core CPI does not include energy and food to reflect the long-run trends. The headline CPI includes eight categories,including food,tobacco and alcohol,apparel,shelter,appliance and services,transportation,education and communication,recreation,medical care,and other commodities and services. As a thumb rule,the headline CPI can be categorized as four groups: the goods (consisting of apparel,automobiles,tobacco,etc.),services (consisting of health care,recreation,education and communication,etc.),shelter (consisting of rent and owners' equivalent rent),and non-core CPI (composed of energy and food prices). They are driven by different economic forces respectively.
Core commodity CPI is closely related to the global value chain
This July,the year-to-year increase in the core commodity CPI fell to 6.9% from 12.4% in February,but was still among the high level since 1975. For decades,the globalized industrial chain has continued to expand the world market boundaries. Among them,Japan,Republic of Korea,Singapore,China’s Taiwan and Hong Kong,the Southeast Asia have benefited successively,taking the advantage of the rich labor force. In the industrial chain,final products sold to the US at lower prices. After China joined the WTO in 2001,this chain becomes more sophisticated and well functional. For a long time,it greatly depressed the price of commodities in the U.S. According to one research by NBER,with China's accession to the WTO,between 2000 and 2006,China's exports lowered the price of the US industrial products by 7.6% annually. The US multinational giants such as Wal-Mart have been using the global chain to improve total factor productivity and reduce the labor compensation. Besides,the great relocation of manufacturing has also reduced the bargaining power of the local labor force in the US to a big extent. From 2000 to 2021,the average year-to-year increase in the US commodity CPI was only 0.58%,and the proportion of labor income dropped by 3 percentage points from 5.67%.
Since the global pandemic of the COVID-19,the supply chains of East Asian manufacturing countries such as China and Republic of Korea have been interrupted several times,and the supply of important intermediate products such as auto parts has been in shortage,resulting in a tight supply. When goods arrived in the US ports,transportation is jammed by the shortage of dock-men and truck-drivers,because they are well subsidized and less willing to work. Moreover,the tariffs imposed by the Trump Administration on China have not been completely removed,and the political measures to restrict the export of technology and key components to China still exist. As a result,the well-functioning global chain over the past 20 years is facing sluggish supply,rising costs,and political risks. This pushed up the prices of the US commodities. For example,new car prices have risen more than 15% since last April,the highest level since World War II.
CPI of the core services is closely related to labor supply.
Since the outbreak of COVID-19 pandemic,the year-to-year increase in the core commodity CPI has been on an upward trend,rising from 1.1% in May 2020 to 6.9% this June,and then fell slightly to 6.8% in July.
Services are highly non-tradable and mainly driven by the elasticity of domestic labor supply. Based on the difference in skills,services can be roughly divided into high-skilled and low-skilled. The former are the professional such as medical care,while the latter includes general services such as restaurants,hotels,and retail. Due to the globalization,the financial and information firms expanded greatly and have always accounted for about 10% of the employees. However,the aging population has led to a substantial increase in employment in health care. For a long time,the growth rate of the health price has been higher than the headline CPI. The more significant change in this economic cycle is the booming in low-skilled service employment. Since the 1970s,the low-skilled service has provided a large number of jobs,and accounting for 9% of the employees to as large as 17.2% in 2022. It is also the industry that has created the most jobs this year.
The current round of the epidemic has greatly increased the market's demand for low- and medium-skilled labor. As a result,it reduced the long-term unemployed to a historical low level,and more surprisingly,some people who had left the job market now come back to seek a job. In April 2020,the labor force fell by 6.4 million to 156 million,but since then,the demand for low-skilled jobs has continued to grow,driving the job market to add 8.05 million new labor forces within one year. This means that some non-labor population (voluntary unemployment) has been attracted into the market,which has continuously pushed the new employment numbers to surprise the market expectations. For example,the number of non-farm payrolls increased by 528,000 in July,far exceeding the market expectations of 258,000. However,it should be noted that the number of labor force began to fluctuate after reaching a peak of 164.4 million this March.
Shelter CPI is mainly limited by insufficient housing supply
Shelter prices rose 7.4% year-to-year in July,contributing to the 37% of the CPI increase. The weight of the Shelter item in the U.S. CPI is as high as 42%,including both the rent of the tenant (5.8%) and the “owner’s equivalent rent” paid by the owner to himself (23.4%),and the rest is services (accounting for 12.8%). The tenant’s rent is the market price and can be observed directly,while the owner’s equivalent rent is usually estimated by the owner,relatively smooth and subject to the calculation errors,but reflects the overall misrepresentations of shelter prices. The US real estate market is highly developed,and home purchase decisions are mainly based on the investment needs and shelter needs. The benchmark interest rate

