Review of the RMB Exchange Rate in 2023 and its Future Prospects
During the first eight months of this year,the RMB exchange rate fluctuated in both directions before experiencing a depreciation. Though the US Dollar Index (USDX) seesawed lower,the RMB continued to depreciate significantly against the USD. The primary cause of the current devaluation of the RMB is the slowdown of domestic economic restoration,while the ongoing monetary tightening cycle of the Federal Reserve (Fed) is also contributing to the RMB’s depreciation. In addition,the regulator has demonstrated a high tolerance for exchange rate depreciation,allowing for greater flexibility in monetary policy regulation. Since entering the second half of the year,the planned policies aim to stimulate economic growth,which is expected to stabilize the RMB exchange rate. As the Fed nears the end of its rate hike,external factors will exert less pressure on the RMB exchange rate. Additionally,the regulator has various exchange rate management tools to ensure the smooth market functioning. It is expected that the RMB exchange rate will maintain a stable two-way fluctuation pattern.
Review of the RMB Exchange Rate Dynamics in the First Eight Months of 2023
In 2023,the RMB exchange rate fluctuated in both directions and then depreciated. By the end of August,the RMB depreciated 4.65% against the US dollar from the end of the previous year,while the USDX raised 0.13% over the same period. Upon reflection on the initial eight months,the RMB exchange rate has gone through three major stages.
The first stage: from the beginning of 2023 to early May,the RMB exchange rate fluctuated in both directions. This stage can be subdivided into two sub-phases. The first sub-phase is from the beginning of 2023 to mid-March,when the USDX experienced sharp fluctuations,and the USDX and USD/CNY trends were closely aligned. During the second sub-phase,which lasted from late March to early May,the USDX seesawed lower,while the RMB experienced a slight depreciation.
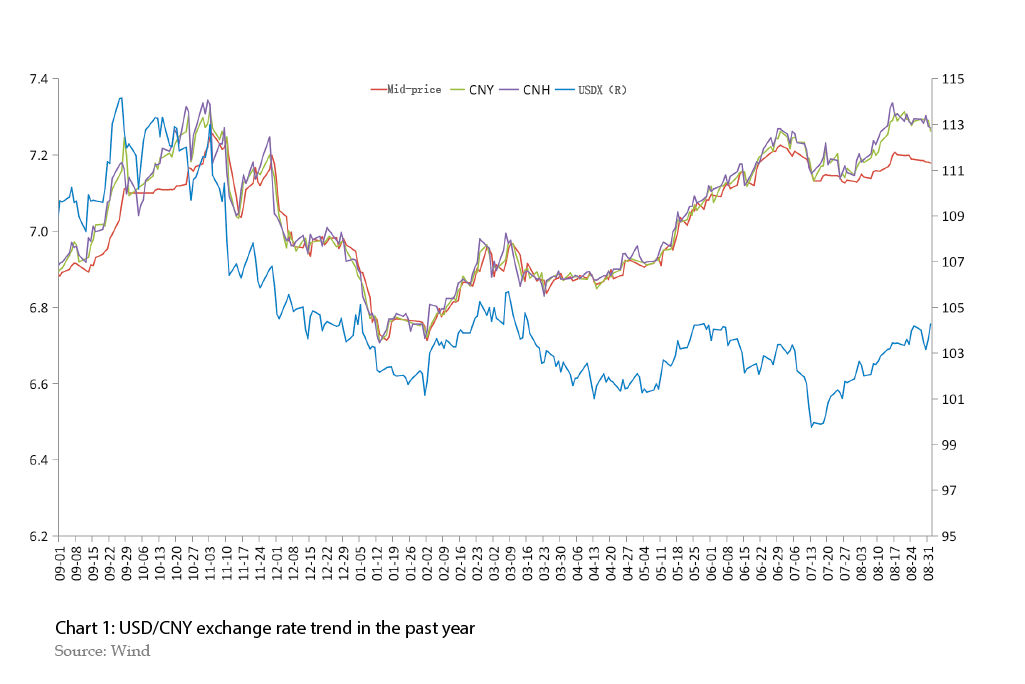
The second stage: the RMB exchange rate depreciated rapidly from mid-May to late June. From May 11,anticipation of the Fed’s rate hike increased,resulting in a significant increase in the USDX. The RMB was subject to passive pressure. By mid-May,both onshore and offshore RMB exchange rate plunged beyond 7 per dollar. In June,the USDX fell. And the onshore and offshore RMB exchange rates fell to 7.2730 and 7.2855,respectively.
The third stage: the RMB exchange rate has returned to a stable two-way fluctuation pattern since July. In the first half of July,the regulator attempted to stabilize the exchange rate,and the USDX and external pressure once weakened,resulting in the eventual stabilization and rebound of the RMB. Since mid-to-late July,the regulator has increased the macro-prudential adjustment parameters for cross-border financing,sending additional signals of exchange rate stability. Despite the significant rebound of the USDX,the RMB exchange rate remained a stable two-way fluctuation pattern due to the CPC Central Committee’s Politburo meeting,which boosted market confidence.
In general,the RMB exchange rate index (CFETS) and the USD/CNY exchange rate displayed comparable trends,indicating that domestic factors have had a stronger impact on changes in the RMB exchange rate since the beginning of this year,while fluctuations in the USD have only had a catalytic effect.
Analysis of Current RMB Exchange Rate Depreciation
The Domestic Slowdown in Economic Recovery
China’s economy has shown signs of recovery this year,though it has been slower than market expectations. Insufficient demand was a major issue. China has entered a new phase of COVID-19 response at the beginning of 2023,resulting in surging domestic and international market confidence. There was a significant rise in stock indexes in January,and Shanghai-Hong Kong Stock Connect experienced a net purchase of northbound funds for 17 consecutive trading days. As economic data was released month by month,the market’s appraisal of the domestic economic recovery became more realistic,resulting in downward expectations and pressure for the RMB to depreciate.
China’s GDP grew 5.5% year-on-year in the first half of the year,considerably faster than the growth rate of the entire last year and the first quarter of this year. However,this was less than many organizations had anticipated at the beginning of 2023. Upon the release of the first quarter’s economic data,certain indicators revealed a decline in growth relative to the preceding period. Investment and real estate-related indicators experienced a more significant decline. In the first half of the year,total retail sales of consumer goods grew rapidly,while communication equipment,home appliances,and other durable consumer items performed less well. Official PMI and Caixin PMI had been declining since March,and both dropped below the 50-point threshold in April,according to leading indicators. Until August,official PMI was below the 50-point threshold. Overall,the economic recovery began to show a slower pace than expected in the mid-late period of March,which was further confirmed after the release of the data for the first quarter,thus activating the downside channel of the RMB exchange rate.
Weak exports and foreign investment may increase the volatility of the RMB exchange rate. The cumulative rate of export growth was positive in the first four months of 2023,but the situation deteriorated again in May. In January of this year,the actual use of foreign capital displayed growth but subsequently declined. The concurrent decline in exports and foreign investment would not only directly impact the balance of payments and foreign exchange settlements,but it may also indirectly exacerbate the instability of the RMB exchange rate by affecting market confidence.
The Fed’s Tightening Cycle
Since the beginning of this year,the Fed’s cycle of monetary tightening has continued. According to the Fed’s December 2022 dot plot,the median projected policy rate at the end of 2023 was between 5 and 5.25%. However,following a rate hike in July,the US policy rate has risen from5.25% to 5.50%,reaching its highest level in 22 years. As a result of unanticipated changes in US economic data,market forecasts for a Fed rate hike have shifted dramatically,causing USDX fluctuations.
The Fed’s ongoing rate hike brings external disturbances to the RMB exchange rate from two aspects.
Initially,the USDX’s volatility caused fluctuations in the RMB. Specifically,the RMB depreciated as the US dollar strengthened in the second stage. This year,the USDX has experienced three waves of strengthening that have caused significant fluctuations in the RMB exchange rate. During the second wave of appreciation of the US dollar,it was anticipated that the domestic economic recovery would falter,resulting in a signifi

