The RMB Exchange Rate Will Most Likely Fluctuate Within a Reasonable Range
The year 2021 witnessed the steady recovery of China's economy and the smooth running of the financial market. The renminbi exchange rate against the US dollar fluctuated within a reasonable range,going through three stages of falling,rising,and fluctuating. In 2022,the renminbi exchange rate will face depreciation pressure considering the increasing downward pressure on China's economy,the likely slowdown in the external demand growth,and the normalization of the Federal Reserve(Fed)'s monetary policy. However,it will still likely fluctuate within a reasonable range thanks to the resilience of China’s economy and sufficient policy control tools of the government.
Review of the Renminbi Exchange Rate Trend in 2021
In 2021,the renminbi exchange rate against the US dollar generally remained stable and fluctuated within a reasonable range. As of November 16,the central parity rate of the renminbi against the US dollar was 6.3924,an appreciation of about 1.34% from the beginning of the year (to be updated). The fluctuation of the renminbi exchange rate showed an atypical "M"-shaped trend throughout the year,including three stages of falling,rising,and oscillating (See Figure 1).
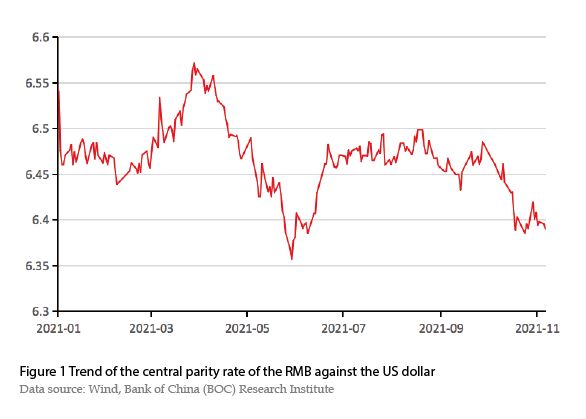
Stage I: From the beginning of 2021 to the end of March,the renminbi depreciated amid volatility. The central parity rate of the renminbi against the US dollar fell from 6.4760 to 6.5713,a slight depreciation of about 1.45% due to the strong revitalization of the US economy,the upward trend of the US dollar index,and the narrowing of the interest rate gap between China and the US.
Stage II: From the beginning of April to the beginning of June,the renminbi continued to appreciate. The central parity rate of the renminbi against the US dollar rose from 6.5584 in early April to 6.3572 in early June,an appreciation of 3.16% as a result of the weakening of the US dollar,the accelerated inflow of cross-border capital,and the good start of the China’s economy.
Stage III: From the beginning of June to the end of the year,the renminbi exchange rate fluctuated within a narrow range. In early June 2021,the People's Bank of China (PBC) announced that it would raise the foreign exchange deposit reserve ratio from 5% to 7% from June 15,which helped to stabilize market expectations and rationalize the willingness of market players to settle and sell foreign exchange. Therefore,since June,the renminbi exchange rate against the US dollar had hovered around 6.46,but after October,the renminbi appreciated slightly and broke through the 6.4 mark.
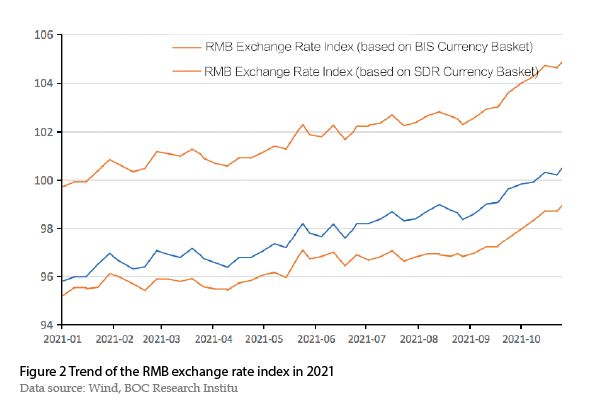
The renminbi exchange rate index went up in general. In 2021,the renminbi exchange rate index of the China Foreign Exchange Trade System (CFETS),Bank for International Settlements (BIS) currency basket and Special Drawing Rights (SDR) currency basket rose from 95.80,99.73 and 95.20 at the beginning of the year to 100.83,105.15 and 99.21 on November 5,an increase of 5.25%,5.43% and 4.21% respectively (Figure 2),indicating that the renminbi was relatively strong among the major non-US currencies in the world. This mainly owes to the steady recovery of China’s economy,which performed better than most economies,and the stronger overall attractiveness of the renminbi assets in the world.
Analysis on Factors Affecting RMB Exchange Rate in 2021
First,the Chinese economy recovers with a slowly falling growth rate. The long-term trend of exchange rates is mainly determined by economic fundamentals,the basic factor accounting for the fluctuation. Economic growth affects the exchange rate through the path of “gross domestic product (GDP) growth - rising investment profitability - increasing capital inflows - exchange rate appreciation”. In 2021,China’s economy maintained a steady recovery. In the first three quarters,GDP increased by 9.8% year-on-year,with an average growth rate of 5.2% in the two years. The GDP growth rate in the first three quarters went from high to low: in the first,second and third quarters,GDP increased by 18.3%,7.9% and 4.9% year-on-year respectively,with an average growth rate of 5%,5.5% and 4.9% in the two years. The strong performance of external demand played a pivotal role in driving China’s economy. In the first three quarters of 2021,exports increased by 33% cumulatively,with an average growth rate of 14.65% in the two years,significantly higher than the level in the same period in 2019. Domestic demand maintained a weak recovery,with the growth rate slowing down in the third quarter. In the first three quarters,the total retail sales of consumer goods and fixed asset investment rose by 16.4% and 7.3% year-on-year respectively; the average growth rates in the two years were 3.9% and 3.8% respectively,0.5 and 0.6 percentage points lower than the first half of the year.
Second,the expansion of the balance of payments surplus helped stabilize the renminbi exchange rate. Changes in the balance of payments affect the foreign exchange market of an economy,which will further shape the trend of the currency exchange rate. In 2021,China’s balance of payments surplus expanded notably,laying a solid foundation for the relatively strong performance of the renminbi among the global non-USD currencies. Firstly,the trade surplus in goods increased. In the first three quarters of 2021,China’s trade surplus in goods reached US$379.6 billion,up by 16% year on year. Secondly,the trade deficit in services narrowed. In the first three quarters of 2021,China’s trade deficit in services was US$82.1 billion,a year-on-year decrease of 30%. Thirdly,the direct investment produced a large surplus. In the first three quarters of 2021,the net inflow of China’s direct investment amounted to US$163.6 billion mainly due to the continuous improvement of China’s economy,which enhanced the confidence of foreign investment in China.
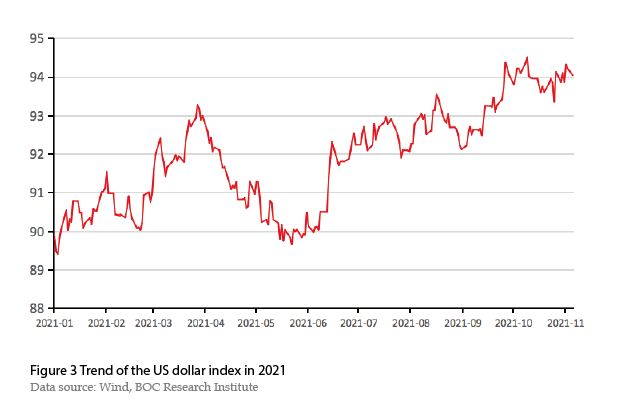
Third,with the strong revitalization of the US economy,the US dollar index went up amid volatility. Historically,the renminbi exchange rate against the US dollar and the US dollar index,which has a substantial impact on the former,ebbed and flowed. In 2021,with the promotion of vaccines and the control of the pandemic,the US economy showed a momentum of rapid recovery,backing up the overall increase of the US dollar index,up by 4.64% from 89.88 in early 2021 to 94.05 in mid-November (Figure 3). In the first quarter of 2021,as the US economy was doing much better than Europe,the US dollar index climbed gradually,and the renminbi exchange rate fluctuated and depreciated. In the second quarter,the US dollar index turned from strong to weak because of the accelerated economic recovery in Europe,the lower-than-expected economic indicators such as the unemployment rate in the US,and the Fed’s dovish attitude toward the loose monetary policy against the backdrop of higher inflation. However,the US dollar index rose again after the third quarter due to factors such as the Fed’s tapering of bond purchases. This weakened the pressure of renminbi appreciation,and the renminbi exchange rate against the US dollar entered a period of narrow fluctuation after June.
Fourth,expectations of the foreign exchange market were stable on the whole,except for shocks caused by fluctuations at some time points. The behavioral finance theory believes that human psychological factors have a massive impact on market behavior. Accordingly,market sentiment fluctuations will lead to changes in the behavior of market entities,which will further affect the exchange rate trend. In 2021,despite the overall stable expectations of renminbi exchange rate,the expectation of unilateral appreciation was formed in May,with many investors following the herd. From May 25th to 28th,the daily average transaction volume of spot inquiries in the interbank market exceeded US$47 billion,7.06% higher than the average in December 2020. The 1-year non-deliverable forward (NDF) also implied that the renminbi would apprecia

